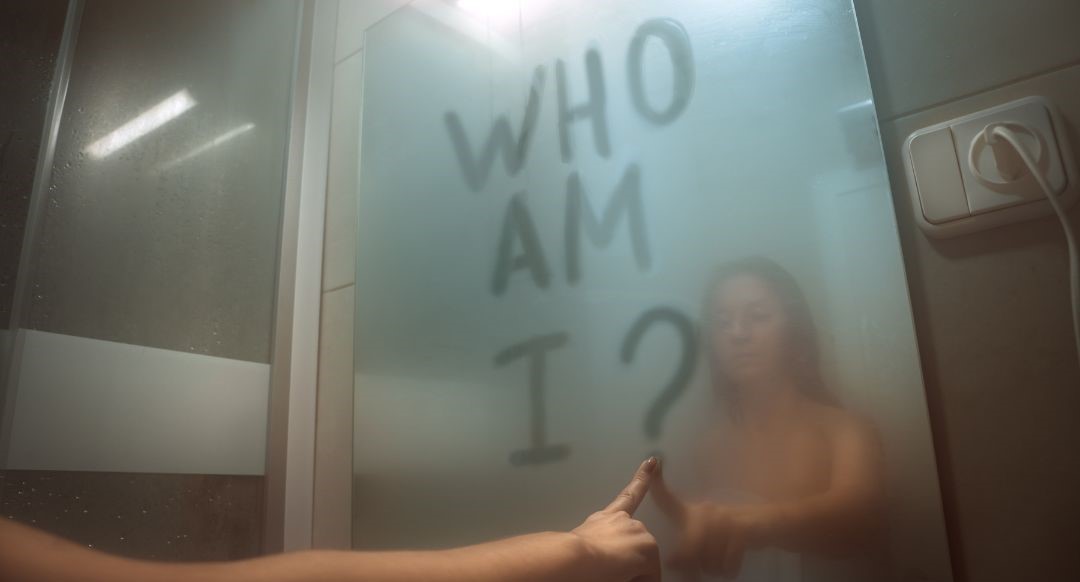In the pursuit of personal growth and emotional well-being, the concept of self-awareness stands as a cornerstone—a pathway toward understanding oneself on a deeper level. However, despite its significance, achieving self-awareness is often a challenging and intricate journey, riddled with complexities that make introspection and self-reflection a difficult task. Let’s explore the intricacies behind why self-awareness can be a challenging endeavor.
Why Self-Awareness is Difficult
Complexity of the Human Psyche: The human mind is intricate and multifaceted, making it challenging to navigate and comprehend all its layers and nuances. The human mind is a vast and dynamic landscape, shaped by a myriad of influences including genetics, upbringing, culture, and life experiences, which can make unraveling its intricacies a daunting task.
One of the complexities of the human psyche lies in its ability to harbor both conscious and unconscious processes. While individuals may have some awareness of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, there are often underlying beliefs, fears, and motivations that operate at a subconscious level, influencing behavior without conscious awareness. Untangling these unconscious patterns requires a deep level of introspection and self-reflection, which can be challenging to access without intentional effort.
Furthermore, the human psyche is inherently multifaceted, consisting of layers of identity, emotions, and cognitive processes that interact in complex ways. Individuals may grapple with conflicting emotions, contradictory beliefs, or ambivalent desires, which can create internal discord and make it difficult to discern one’s true feelings or motivations. Additionally, the ever-changing nature of the psyche means that self-awareness is not a static state but rather a continuous process of exploration and discovery.
Emotional Baggage and Defense Mechanisms: Past experiences, traumas, or defense mechanisms often obscure self-awareness, creating barriers to understanding our true emotions or motivations. Defense mechanisms indeed pose significant barriers to self-awareness, as they are psychological strategies that individuals unconsciously employ to cope with uncomfortable emotions, thoughts, or situations. These mechanisms serve to protect the ego from anxiety, distress, or threats to self-esteem, but they can also obscure genuine self-awareness by distorting perceptions, rationalizing behaviors, or deflecting responsibility.
One common defense mechanism is denial, where individuals refuse to acknowledge or accept painful truths or aspects of themselves, instead opting to minimize or ignore uncomfortable feelings or experiences. Denial can prevent individuals from confronting difficult emotions or addressing underlying issues, hindering their ability to cultivate genuine self-awareness.
Another defense mechanism is repression, which involves pushing distressing thoughts, memories, or emotions into the unconscious mind, effectively blocking them from conscious awareness. While repression may provide temporary relief from discomfort, it can also create barriers to self-awareness by obscuring important insights or hindering emotional processing.
Rationalization is another defense mechanism that involves creating logical explanations or justifications for one’s thoughts, feelings, or behaviors, often to protect self-esteem or avoid feelings of guilt or shame. While rationalization may provide a sense of cognitive closure, it can also prevent individuals from exploring deeper motivations or understanding the underlying causes of their actions.
Projection is yet another defense mechanism where individuals attribute their own unacceptable thoughts, feelings, or impulses to others, effectively externalizing internal conflicts or anxieties. By projecting onto others, individuals may avoid confronting uncomfortable truths about themselves, thereby impeding their ability to gain genuine self-awareness.
These defense mechanisms, along with others such as repression, displacement, and reaction formation, create barriers to self-awareness by distorting perceptions, inhibiting emotional processing, and deflecting responsibility. Overcoming these barriers requires a willingness to confront uncomfortable truths, cultivate curiosity and self-reflection, and develop healthier coping strategies that foster genuine self-awareness and emotional resilience. Through introspection, therapy, and self-compassion, individuals can gradually dismantle these defenses, allowing for deeper self-awareness, personal growth, and authentic self-expression.
Subjectivity and Bias: Biases, perceptions, and preconceived notions can cloud self-awareness, hindering an objective understanding of oneself. Subjectivity refers to the inherent influence of personal perspectives, beliefs, and emotions on one’s interpretation of reality, while bias involves preconceived notions, stereotypes, or prejudices that shape individuals’ judgments and decisions.
One of the challenges of self-awareness lies in navigating the subjective nature of perception, as individuals’ understanding of themselves is inherently shaped by their unique perspectives, experiences, and cultural backgrounds. These subjective lenses can color individuals’ perceptions of their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, leading to distortions or inaccuracies in self-assessment. For example, individuals may interpret ambiguous situations in ways that align with their existing beliefs or expectations, rather than objectively assessing the situation.
Bias further complicates the process of self-awareness by influencing individuals’ judgments and evaluations of themselves. Whether stemming from societal influences, past experiences, or internalized attitudes, biases can distort individuals’ self-perception and contribute to feelings of inadequacy, insecurity, or self-doubt. For example, individuals may internalize negative stereotypes or societal norms, leading them to judge themselves harshly or adopt unrealistic standards of perfection.
Moreover, individuals may exhibit cognitive biases such as confirmation bias, where they selectively attend to information that confirms their existing beliefs or self-image, while ignoring or discounting contradictory evidence. This can create a skewed perception of oneself and hinder the ability to accurately assess strengths, weaknesses, or areas for growth.
Addressing subjectivity and bias in self-awareness requires a commitment to introspection, self-reflection, and humility. By acknowledging the limitations of one’s perspective and actively seeking feedback from others, individuals can gain a more balanced and nuanced understanding of themselves. Additionally, cultivating mindfulness and metacognition can help individuals become more aware of their own thought patterns, biases, and automatic reactions, allowing them to approach self-assessment with greater objectivity and openness.
Fear of Uncovering Uncomfortable Truths: Delving into personal vulnerabilities or uncomfortable truths can evoke fear or discomfort, deterring introspection. individuals may instinctively avoid confronting aspects of themselves that provoke feelings of shame, guilt, or vulnerability. This fear can manifest as resistance to introspection, denial of difficult emotions, or avoidance of challenging experiences, ultimately hindering individuals’ ability to gain deeper insights into their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
One of the primary reasons individuals fear uncovering uncomfortable truths is the potential threat to their self-image or identity. Confronting aspects of oneself that are inconsistent with one’s idealized self-concept can trigger feelings of inadequacy, unworthiness, or self-doubt, leading individuals to resist acknowledging or accepting these aspects of themselves. Additionally, individuals may fear the potential consequences of self-awareness, such as facing difficult decisions, making changes, or confronting painful emotions, which can be daunting and overwhelming.
Moreover, the fear of uncovering uncomfortable truths may be compounded by societal expectations, cultural norms, or personal beliefs that stigmatize vulnerability or imperfection. Individuals may internalize messages that equate success or worthiness with perfection, leading them to avoid acknowledging or addressing their struggles, failures, or insecurities.
External Influences and Societal Norms: External influences, societal expectations, or cultural norms might shape self-perception, making it challenging to discern personal beliefs from societal conditioning. These external factors can exert powerful influence on individuals’ self-concept, self-esteem, and sense of identity, often obscuring genuine self-awareness and authentic self-expression.
One way external influences hinder self-awareness is through the perpetuation of unrealistic ideals or standards of success, beauty, or achievement. Whether through media, advertising, or social comparisons, individuals are bombarded with messages that promote narrow definitions of success or worthiness, leading them to measure their self-worth against external benchmarks rather than their own intrinsic values or aspirations.
Moreover, societal norms and expectations can shape individuals’ beliefs about what is acceptable or desirable in terms of behavior, relationships, or identity. These norms may reinforce stereotypes, prejudices, or gender roles that limit individuals’ sense of autonomy, authenticity, and self-expression. Individuals may conform to these norms out of fear of rejection or judgment, rather than exploring and embracing their own unique identities and desires.
Additionally, external influences such as family dynamics, cultural traditions, or peer pressure can further complicate the process of self-awareness by shaping individuals’ perceptions of themselves and their roles within their social contexts. For example, individuals may internalize familial expectations or cultural values that conflict with their own personal beliefs or aspirations, leading to feelings of confusion, guilt, or self-doubt.
Barriers to Self-Awareness
Denial or Avoidance: Individuals might consciously or unconsciously avoid confronting certain aspects of themselves due to discomfort or fear. Denial involves refusing to acknowledge or accept reality, while avoidance entails actively avoiding situations, thoughts, or emotions that provoke discomfort or distress. Both defense mechanisms serve to protect individuals from experiencing pain or anxiety, but they also hinder the process of self-discovery and personal growth.
One of the challenges of denial is that it prevents individuals from facing difficult truths about themselves or their circumstances. Whether it’s denying the existence of a problem, minimizing its severity, or blaming external factors, denial allows individuals to maintain a sense of security or control by avoiding uncomfortable realities. However, this avoidance perpetuates a cycle of ignorance and stagnation, preventing individuals from addressing underlying issues or making meaningful changes in their lives.
Similarly, avoidance prevents individuals from engaging in introspection or self-reflection by diverting their attention away from uncomfortable thoughts, emotions, or experiences. Whether through distractions such as work, social media, or substance use, avoidance allows individuals to temporarily escape feelings of anxiety, sadness, or self-doubt. However, this avoidance only serves to perpetuate emotional avoidance and prevent individuals from gaining insight into their inner world.
Furthermore, denial and avoidance can prevent individuals from seeking feedback or support from others, as they may fear facing criticism or judgment. This lack of external perspective further reinforces the barriers to self-awareness, as individuals remain isolated in their own subjective experiences without the opportunity for growth or learning.
Lack of Introspection: Busy lifestyles or distractions can hinder introspection, preventing individuals from dedicating time for self-reflection. Introspection involves looking inward and examining one’s own thoughts, feelings, and motivations, but when individuals fail to engage in this process, they may remain unaware of their true selves and the factors influencing their actions and decisions.
One of the challenges of lacking introspection is that it limits individuals’ ability to recognize patterns, triggers, or underlying beliefs that may be driving their behavior. Without taking the time to reflect on their experiences or explore their inner world, individuals may continue to repeat unproductive patterns or react impulsively to situations without understanding the root causes of their actions.
Moreover, lacking introspection can prevent individuals from identifying areas for growth or recognizing opportunities for personal development. Without taking the time to examine their strengths, weaknesses, and areas of improvement, individuals may remain stagnant or resistant to change, hindering their ability to reach their full potential or achieve their goals.
Additionally, lacking introspection can lead to a sense of disconnection or alienation from oneself, as individuals may feel disconnected from their own thoughts, emotions, or values. This can contribute to feelings of emptiness, dissatisfaction, or existential angst, as individuals struggle to find meaning or purpose in their lives without a deeper understanding of themselves.
Inconsistent Feedback: Inconsistent or biased feedback from others might create discrepancies between self-perception and reality. Feedback serves as a mirror through which individuals gain insight into their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth, but when feedback is inconsistent or contradictory, it can hinder individuals’ ability to form a coherent understanding of themselves.
One of the challenges of inconsistent feedback is that it can create ambiguity and uncertainty regarding one’s self-concept or identity. For example, if individuals receive conflicting feedback about their strengths or abilities from different sources, they may struggle to discern which perceptions are accurate or reliable, leading to feelings of confusion or self-doubt.
Moreover, inconsistent feedback can undermine individuals’ confidence in their own judgment or intuition, as they may question their own perceptions or interpretations of their experiences. This can erode individuals’ sense of self-trust and self-reliance, making it difficult for them to cultivate genuine self-awareness or make decisions aligned with their values and aspirations.
Furthermore, inconsistent feedback can perpetuate feelings of inadequacy or imposter syndrome, as individuals may struggle to internalize positive feedback or dismiss it as insincere or untrustworthy. Conversely, negative feedback may be amplified or internalized, reinforcing negative self-perceptions or beliefs.
Overidentification with Thoughts and Emotions: Overattachment to thoughts or emotions can blur the line between oneself and these transient experiences. When individuals become overly fused with their thoughts and emotions, they may lose sight of their underlying values, beliefs, and identity, leading to a distorted perception of themselves and the world around them.
One of the challenges of overidentification with thoughts and emotions is that it creates a sense of entanglement or fusion with one’s internal experiences. Instead of recognizing thoughts and emotions as passing mental events, individuals may perceive them as absolute truths or reflections of their identity, leading to overgeneralization or catastrophizing. For example, individuals may interpret fleeting feelings of sadness as indicative of their entire self-worth, or perceive critical thoughts as undeniable evidence of personal failure.
Moreover, overidentification with thoughts and emotions can lead to rumination or repetitive patterns of negative thinking, as individuals become trapped in cycles of self-criticism, worry, or self-doubt. This rumination perpetuates a cycle of emotional distress and reinforces negative self-perceptions, making it difficult for individuals to gain perspective or insight into their experiences.
Furthermore, overidentification with thoughts and emotions can hinder individuals’ ability to respond flexibly to challenges or setbacks. Instead of approaching difficult situations with resilience and adaptability, individuals may react impulsively or defensively based on their immediate emotional reactions, leading to conflict or avoidance.
Navigating the Journey of Self-Awareness
Cultivating Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness aids in observing thoughts, emotions, and behaviors without judgment. One of the key aspects of mindfulness is developing present moment awareness, which involves directing attention to the sensations, thoughts, and emotions occurring in the here and now. Through practices such as meditation, body scan exercises, or mindful breathing, individuals can learn to observe their internal experiences with greater clarity and presence, allowing them to recognize patterns, triggers, or habitual reactions.
Moreover, mindfulness encourages individuals to adopt an attitude of curiosity and acceptance toward their experiences, rather than reacting with judgment or resistance. By cultivating an open and compassionate stance toward themselves, individuals can create a safe inner space for exploring their thoughts and emotions without fear of criticism or self-blame.
Additionally, mindfulness helps individuals develop greater emotional regulation by increasing awareness of the connection between thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations. By noticing how thoughts and emotions manifest in the body, individuals can learn to respond to challenging situations with greater calmness and equanimity, rather than reacting impulsively or defensively.
Furthermore, mindfulness fosters a sense of self-compassion and kindness toward oneself, which is essential for cultivating genuine self-awareness. By approaching oneself with warmth and understanding, individuals can create a supportive inner environment where they feel safe to explore their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth.
Practicing mindfulness regularly allows individuals to deepen their self-awareness over time, as it encourages a gradual unfolding of insight and understanding into one’s inner world. By integrating mindfulness into daily life, individuals can cultivate a greater sense of presence, clarity, and authenticity, leading to enhanced emotional well-being and personal growth.
Seeking Feedback and Support: Seeking unbiased feedback and guidance aids in gaining external perspectives for self-reflection. Seeking feedback and support from others is a valuable practice for cultivating self-awareness, as it provides an external perspective and insight into one’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. By actively seeking feedback and support, individuals can gain valuable insights, identify blind spots, and develop a deeper understanding of themselves and their interactions with others.
One way to cultivate self-awareness through seeking feedback is to solicit input from trusted friends, family members, or colleagues who can provide honest and constructive feedback about one’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth. By inviting others to share their observations and perspectives, individuals can gain valuable insights into how their behavior is perceived by others and identify areas where they may need to make adjustments or improvements.
Additionally, seeking feedback from mentors, coaches, or therapists can provide valuable guidance and support in navigating personal challenges, overcoming obstacles, and fostering personal growth. These individuals can offer expertise, perspective, and accountability, helping individuals gain clarity and insight into their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Furthermore, participating in peer support groups, workshops, or online communities can provide opportunities for individuals to connect with others who may be experiencing similar challenges or struggles. By sharing experiences, insights, and resources with others, individuals can gain validation, support, and encouragement in their journey toward self-awareness and personal growth.
It’s important to approach seeking feedback and support with an open mind and a willingness to receive both positive and constructive feedback. While feedback may sometimes be challenging or uncomfortable to hear, it provides valuable opportunities for growth and self-improvement.
Embracing Vulnerability: Embracing vulnerability fosters openness to uncovering uncomfortable truths and facilitating growth. Embracing vulnerability is a powerful pathway to cultivating self-awareness, as it involves the courage to explore and accept the full range of one’s thoughts, emotions, and experiences without fear of judgment or rejection. By leaning into vulnerability, individuals can deepen their understanding of themselves, uncover hidden truths, and foster authentic connections with others.
One of the key aspects of embracing vulnerability is acknowledging and accepting one’s imperfections, insecurities, and limitations. Rather than striving for perfection or hiding behind a facade of strength, vulnerability involves being open and honest about one’s struggles, fears, and uncertainties. By embracing vulnerability, individuals create a safe inner space where they can explore their innermost thoughts and emotions with compassion and curiosity.
Moreover, vulnerability involves acknowledging and expressing emotions authentically, even when they are uncomfortable or challenging. Rather than suppressing or denying difficult emotions, individuals can cultivate self-awareness by allowing themselves to fully experience and process their feelings without judgment or criticism. By embracing vulnerability, individuals can gain insight into the underlying causes of their emotions and develop healthier coping strategies for managing them.
Additionally, vulnerability involves being open to receiving feedback and support from others, even when it requires admitting mistakes or seeking help. Rather than viewing vulnerability as a sign of weakness, individuals can recognize it as a strength that fosters connection, empathy, and understanding. By embracing vulnerability in their relationships, individuals can deepen their connections with others and gain valuable insights into their own thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Furthermore, vulnerability involves taking risks and stepping outside of one’s comfort zone in pursuit of personal growth and fulfillment. Whether it’s pursuing a new passion, sharing one’s creative work, or speaking up about one’s needs and desires, vulnerability involves embracing uncertainty and embracing the possibility of failure or rejection. By embracing vulnerability, individuals can cultivate self-awareness by gaining a deeper understanding of their values, passions, and aspirations, and aligning their actions with their authentic selves.
Journaling and Self-Reflection: Journaling or self-reflective practices create space for introspection and understanding. Journaling and self-reflection are powerful practices for cultivating self-awareness, as they provide a structured and intentional way to explore one’s thoughts, emotions, and experiences. By engaging in regular journaling and self-reflection, individuals can gain insight into their inner world, identify patterns or themes in their thoughts and behaviors, and foster personal growth and development.
One of the key benefits of journaling is that it allows individuals to externalize their thoughts and emotions, providing a tangible record of their inner experiences. By putting pen to paper, individuals can gain clarity and perspective on their thoughts and feelings, allowing them to process and make sense of their experiences in a more concrete way.
Moreover, journaling provides a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to explore their innermost thoughts and emotions without fear of criticism or rejection. Whether it’s expressing gratitude, exploring difficult emotions, or setting goals and intentions, journaling allows individuals to be honest and authentic with themselves, fostering a deeper sense of self-awareness and self-acceptance.
Additionally, journaling encourages individuals to engage in self-reflection by asking probing questions, exploring different perspectives, and challenging assumptions. By reflecting on past experiences, successes, and failures, individuals can gain valuable insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth, allowing them to make more informed decisions and navigate life’s challenges with greater resilience and clarity.
Furthermore, journaling can be a tool for tracking progress and growth over time, allowing individuals to see how their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors evolve and change. By regularly reviewing past entries, individuals can identify patterns, trends, or recurring themes in their lives, gaining a deeper understanding of themselves and their experiences.
To get started with journaling and self-reflection, individuals can set aside dedicated time each day or week to write freely about their thoughts, emotions, and experiences. They can also experiment with different journaling prompts, exercises, or techniques to spark creativity and inspiration. Whether it’s through free writing, guided prompts, or structured exercises, journaling can be tailored to fit individual preferences and needs, providing a flexible and versatile tool for cultivating self-awareness and personal growth.
The path to self-awareness is an intricate, often challenging journey, fraught with complexities stemming from the human psyche and external influences. Yet, despite its challenges, the pursuit of self-awareness holds immense value in fostering personal growth, improving relationships, and enhancing decision-making. By embracing vulnerability, seeking introspection, and navigating through barriers, individuals embark on a transformative journey toward a deeper understanding of themselves—a journey that leads to authenticity, personal fulfillment, and a greater connection with oneself and others.

Stacey Alvarez is a Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist (LMFT #101176) with a physical practice in San Jose, California, and serving clients virtually throughout California. Stacey has three college degrees in Psychology and one in Religious Studies. She is an active member of several professional organizations, including the Association for Contextual Behavioral Science (ACBS) and California Association of Marriage and Family Therapists (CAMFT). She specializes in the use of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), and other humanistic approaches to treat adults, teens, couples, and families for issues related with trauma, abuse, anxiety, depression, and relational difficulties.